The type of property you choose can significantly impact your mortgage options, from down payment requirements to interest rates and loan terms. Here’s how different property types affect your mortgage:
1. Primary Residence
- Definition: A primary residence is the home where you live most of the time, such as a single-family home, condo, or townhouse.
- Mortgage Options:
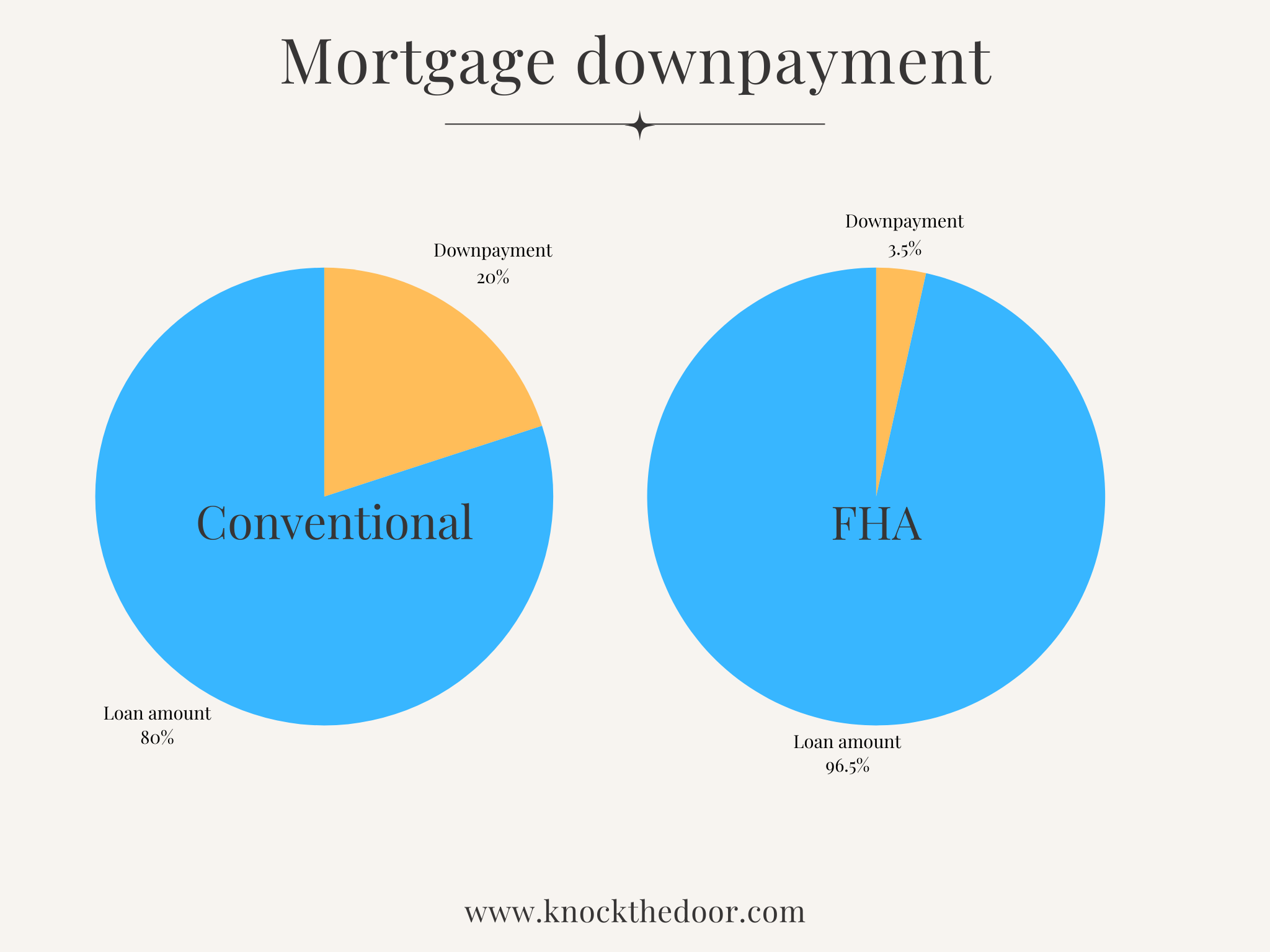
- Down Payment: Can be as low as 3% for conventional loans, 0% for VA loans (for eligible veterans), or 3.5% for FHA loans.
- Interest Rates: Typically, primary residences have the lowest interest rates, as they are considered lower-risk by lenders.
- Loan Terms: More favorable terms and higher loan limits; lenders offer the most flexible terms for primary residences.
- Mortgage Insurance: Mortgage insurance may be required for loans with less than a 20% down payment on conventional loans, but options to remove PMI after reaching 20% equity are available.
2. Second Home / Vacation Home
- Definition: A second home is a property occupied by the owner part-time, often located in a resort area, city center, or other desirable area.
- Mortgage Options:
- Down Payment: Usually higher, typically 10% or more, depending on the lender and market conditions.
- Interest Rates: Rates are often slightly higher than for primary residences, as lenders consider second homes to be higher-risk.
- Loan Terms: Typically favorable but slightly stricter than primary residences. Some lenders may require a higher credit score or reserve funds.
- Mortgage Insurance: PMI may be required if the down payment is less than 20%, although PMI is often more expensive for second homes.
3. Investment Property
- Definition: An investment property is a home purchased with the intent to generate rental income or resell at a profit, rather than live in full-time.
- Mortgage Options:
- Down Payment: Typically requires 15%–25% down for a single-unit property; multifamily investment properties may require even higher down payments.
- Interest Rates: Investment properties usually have the highest interest rates, as they are considered the highest-risk property type for lenders.
- Loan Terms: Stricter requirements, including higher credit scores, reserve funds (up to six months of mortgage payments), and often shorter loan terms.
- Mortgage Insurance: Not usually an option; lenders often require a minimum 20%-25% down payment to avoid mortgage insurance altogether on investment properties.
4. Multifamily Properties (2-4 Units)
- Definition: These properties contain two to four separate living units, allowing the owner to rent out part of the property while living in one unit.
- Mortgage Options:
- Down Payment: If purchased as a primary residence, you may qualify for FHA loans with as low as 3.5% down, or 15%-20% down for conventional loans.
- Interest Rates: Rates are usually slightly higher than for single-family homes, as the rental income aspect adds risk.
- Loan Terms: More stringent qualification requirements; multifamily properties may require higher credit scores and proof of stable rental income.
- Mortgage Insurance: PMI is required if down payment is below 20% (for owner-occupied), though premiums are typically higher for multifamily properties.
5. Condominiums and Co-ops
- Definition: Condominiums (condos) are individually owned units within a larger complex, while cooperatives (co-ops) involve buying shares in a corporation that owns the property.
- Mortgage Options:
- Down Payment: Conventional loans for condos often require at least 10%, while FHA-approved condos may allow as low as 3.5% down.
- Interest Rates: Rates can be similar to single-family homes but may vary if the condo association is financially unstable.
- Loan Terms: Lenders require a thorough assessment of the condo or co-op association’s financial health and may reject properties in complexes with high rental rates or financial instability.
- Mortgage Insurance: May be required if the down payment is less than 20% on conventional loans. Certain co-ops may have unique financing requirements, including higher down payments or co-op-specific mortgage options.
6. Manufactured and Mobile Homes
- Definition: Manufactured or mobile homes are factory-built properties that are movable, often requiring specialized loans.
- Mortgage Options:
- Down Payment: Varies by loan type but may require a minimum of 5%-10% for FHA loans or higher for conventional loans.
- Interest Rates: Generally higher than traditional homes due to the perceived higher risk of depreciation.
- Loan Terms: Lenders often require that the home is permanently affixed to land owned by the borrower. Some loans may have shorter repayment terms.
- Mortgage Insurance: FHA and VA loans are common for manufactured homes, which include mortgage insurance costs that vary by loan type.
Summary Table
Key Takeaways
- Primary Residences offer the best terms, with low down payments, lower rates, and flexible mortgage options.
- Second Homes and Investment Properties have stricter requirements due to higher perceived risk, including larger down payments and higher interest rates.
- Multifamily Properties can be financed with lower down payments if owner-occupied but come with more scrutiny on income stability.
- Condos and Co-ops require lender approval of the association’s financial health, affecting mortgage options.
- Manufactured Homes require specific loans, higher rates, and sometimes shorter terms due to their unique nature.
Each property type has unique factors that impact mortgage options, so aligning your choice with your financing goals is essential for securing the best loan terms.
Disclaimer/Disclosures:
The information provided on this website is for general informational and educational purposes only and must NOT be construed as legal, financial, investment or any other expert advice. Real estate investing involves many risks; any content, presentations, pages, blog posts must not be construed as expert advise, results vary based on many many factors and variables.
We make no representations or warranties about the accuracy or reliability of the information provided.
Always consult a licensed expert, real estate professional and/or financial advisor about your real estate and investment decisions.
View our Disclosures, Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions.